I have my little giraffe. And it always accompany me wherever I am. I love you my little Giraffe.
Hope and Dreams
Friday, September 11, 2015
Tuesday, August 10, 2010
WBS DICTIONARY
WBS - Work Breakdown Structure
As part of project management, it is important to create a work breakdown structure (WBS). The WBS helps in structuring groups and organizes deliverable project elements to make the work process easy to manage. This tool helps define the project's discrete work elements or tasks that help organize and define the total work scope of the project.
The tool is graphically represented in a tree structure that shows a subdivision of effort that is required to complete a task. In the course of a project, the WBS is developed by the end objective, successive subdivision into manageable components in terms of size, duration, and responsibility that include all steps necessary to achieve the objective.
WBS Dictionary
A WBS is usually accompanied by a document called a WBS Dictionary. This document elaborates and explains individual components of the WBS. The components could include codes, description of work, responsibilities, schedule milestones, schedule activities, resources, cost estimates, quality requirements, acceptance terms, technical resources, contract information, additional information, etc.
The WBS Dictionary helps understand the nature of the work as each element of the WBS is thoroughly explained with a functional description, post-implementation descriptions, general requirements, relationships, and dependencies. This form is generally filled by the project team and is used by large and complex projects that have many tasks.
The WBS Dictionary sounds complex and complicated. However, once the task is completed, it may prevent many issues that could occur from miscommunication or misunderstandings among the team members as to which tasks fits where in the project. The document helps effective communication among the team members. Finally, the document subdivides each deliverable into small pieces for easy estimation. The document considers each element and defines for the task:
- Unique identifier for each individual task
- Name
- Description
- Predecessors
- Successors
- Desirable end result
- Functional requirement it fulfils
- Technical requirement of completing the task
- Owners
The WBS Dictionary helps a lot when teams are geographically dispersed as it helps in easing communication issues. The document facilitates communications, helps each team member understand the objective of the task, and allows them to be interchangeable. When the project is about to begin, the project manager usually sends the WBS Dictionary to all team members so that they can begin their individual tasks immediately.
When completing the WBS Dictionary, both the project manager and the team members collectively describe how the task fits the requirements and how the requirements fit the project. This helps validate requirements and ensure the work done is directly related to the scope of the project.
In the majority of cases, the WBS Dictionary is an important output of the WBS process as the WBS would not be useful without it. The WBS Dictionary would also help examine the outputs and why they are important.
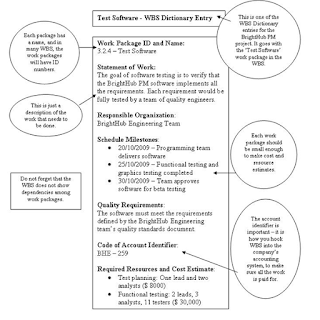
reference : http://www.brighthub.com/office/project-management/articles/52388.aspx
Thursday, July 29, 2010
Typical Project Constraints
Tuesday, July 20, 2010
Masjid Taman Tasik Puteri, Rawang, Selangor
Iskandar Malaysia

Iskandar Malaysia (IM), formerly known as Iskandar Development Region (IDR) and South Johor Economic Region (SJER) is the main southern development corridor in Johor,Malaysia. The Iskandar Malaysia was established on 30 July 2006.
Lebuhraya Karak

Panjang : 60.00 Kilometer
Tarikh dibuka : 30-Apr-1999
Tarikh dibina : 03-Okt-1994
Alamat pejabat : 1, Jalan Batu Caves, 68100 Batu Caves, Selangor Darul Ehsan.
Konsesi MTD Prime Sdn Bhd
Website : www.mtdinfraperdana.com/toll_roads/default.asp
Latar Belakang Projek
Projek ini telah diswastakan kepada MTD Construction Sdn Bhd dan telah dipindahkan (Novate) kepada MTD Prime Sdn Bhd. Ianya bermula dari Kuala Lumpur di km 19.2 dan berakhir di Sungai Dua, Karak, Pahang di km 79.2. Pembinaan bermula pada Oktober 1994 dan siap 4 1/2 tahun selepas itu. Sebagai laluan utama yang menhubungkan antara Pantai Barat Semenanjung dengan Pantai Timur Semenanjung, ianya akan membawa pembangunan kepada persekitarannya.
Fakta Teknikal
Tarikh Mula Konsesi Julai 1994
Tarikh Tamat Konsesi Mei 2021
Tempoh Konsesi 27 Tahun
Panjang 60 km
Persimpanngan Bertingkat 2 buah (Dibina oleh Syarikat Konsesi)
Bil Tol Plaza 2 buah - Plaza Tol Gombak dan Plaza Tol Bentong
Bahagian A
Seksyen 1 - bermula daripada KM 19.20 hingga KM 37.0 (sepanjang 17.8 KM). Tempoh perlaksanaan 33 bulan dan siap pada 27hb. Julai 1997.
Sekyen 2A - bermula daripad KM 37.0 hingga KM. 45.5 (sepanjang 17.8 KM). Tempoh perlaksanaan 43 bulan dan siap pada 27hb. Julai 1997.
Syekyen 2B - bermula daripada KM 45.5 hingga KM 62.3 (sepanjang 16.8 KM). Tempoh perlaksanaan 45 bulan siap pada 27hb. September 1998.
Bahagian B
Seksyen 2C - bermula daripada kilometer 62.3 hingga lkilometer 79.2 (sepanjang 16.8 KM). Tempoh perlaksanaan 53 bulan dan siap pada 27hb. Julai 1999.
Bahagian X
Bahagian X yang bermula daripad kilometer 15.5 hingga kilometer 19.2 akan diserahkan semula kepada JKR kerana terlibat dalam projek Jalan Lingkaran Tengah II bagi pakej III dan IV yang dikendalikan oleh JKR.
